DEVELOPMENTAL JOINT DISEASES
NEUTERING AND JOINT DISEASE
A 2020 study proposed a link between neutering and joint disease. Belgian Malinois were not included, so the table below shows data from German Shepherd dogs.
SPECIFIC CONDITIONS
-
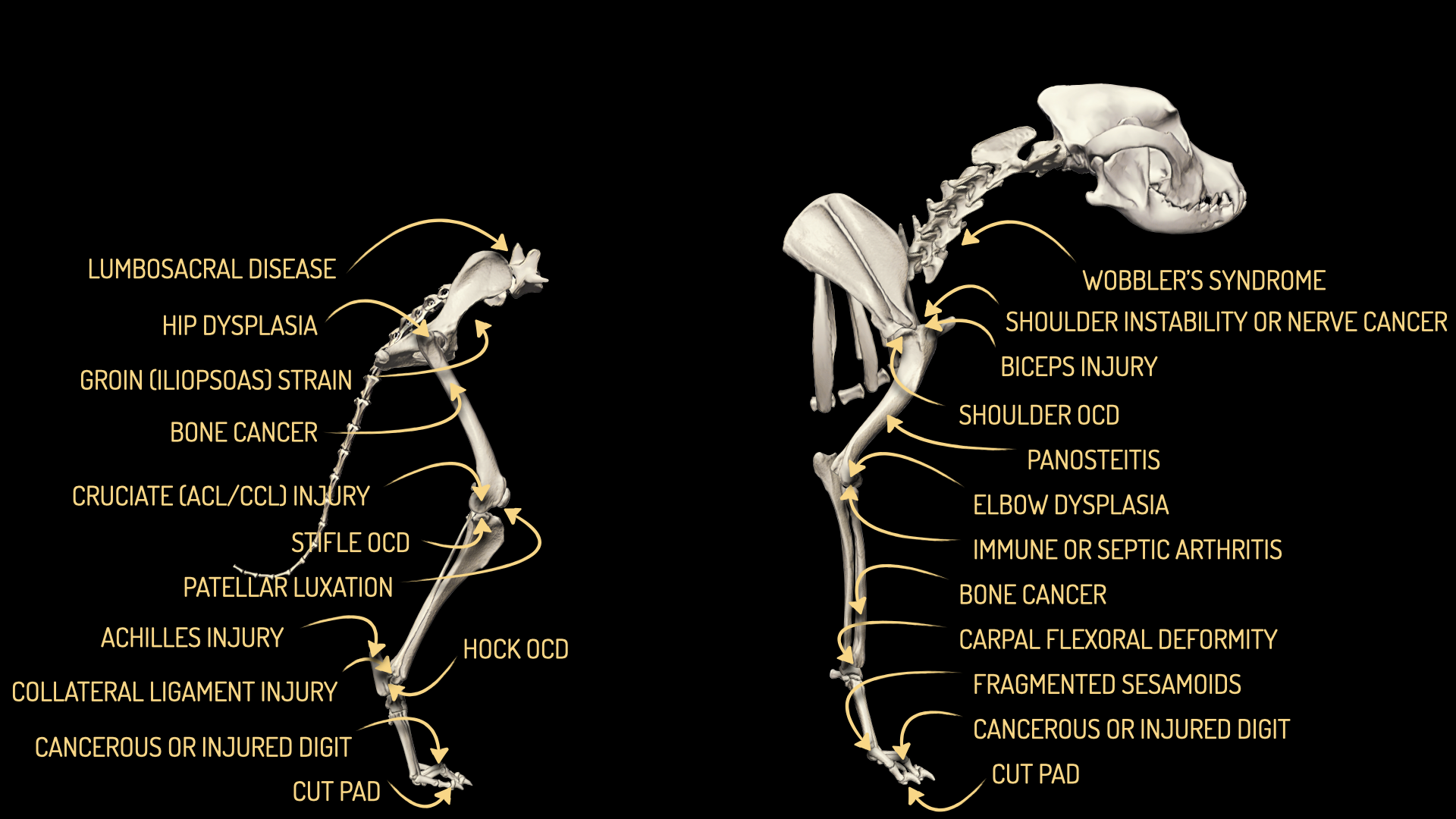
Panosteitis causes cycles of short-term lameness which can switch between limbs. It has several possible causes including consumption of protein-rich, high-calorie commercial puppy food.
Elbow dysplasia is a common cause of lameness in large breed dogs. Ideal treatment depends on severity (which is very variable).
Shoulder OCD involves flaking of cartilage. It’s less common than elbow dysplasia and typically affects rapidly growing puppies.
-
Elbow arthritis secondary to elbow dysplasia gradually progresses over time. Average age at diagnosis in the UK is 6.3 years-old. The best treatment depends on age and arthritis severity.
Chronic shoulder muscle injuries are more likely in sporting dogs. Diagnosis can be challenging.
Treatment of carpal collapse depends on severity. Options include external supports and carpal arthrodesis.
-
A 5.4% incidence of hip dysplasia ranked Malinois #160 in 2020. Mild and moderate hip dysplasia rarely cause significant lameness. Over a ten year period, 8 Malinois hip replacements were registered in a UK database.
Severe pain triggers a suspicion for panosteitis.
-
ACL (CCL) injury is the commonest cause of chronic hindlimb lameness in adults. Tap here to learn more about how to diagnose and treat ACL injuries.
Mild and moderate hip dysplasia rarely cause significant lameness.
Severe pain triggers a suspicion of lumbosacral disease or bone cancer.
Fibrotic myopathy (also called gracilis or semitendinosus muscle contracture) is a non-painful hamstring muscle contracture which causes a characteristic mechanical lameness. Stem cell therapy is a promising treatment.