DEVELOPMENTAL JOINT DISEASES
Rottweilers have a relatively high risk for several bone and joint disorders. Two or more conditions are often present in the same individual.
NEUTERING AND JOINT DISEASE
A series of published by researchers at the University of California proposed a link between neutering and joint disease. The table below shows the Rottweiler data.
SPECIFIC CONDITIONS
-
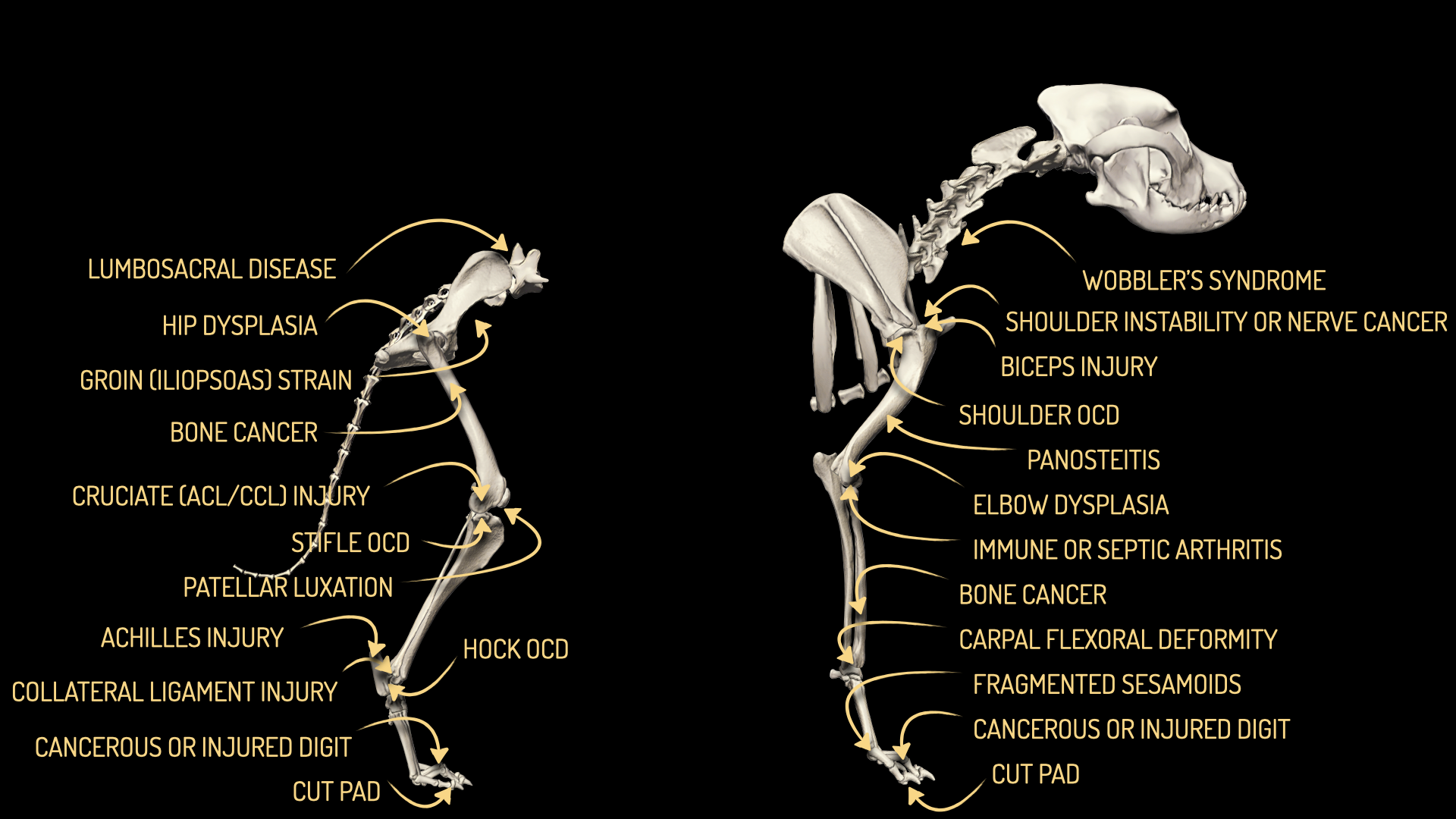
Rottweilers have a high incidence of elbow dysplasia. Risk is 36x higher than average. Chronic forelimb lameness in puppies warrants veterinary investigation. Elbow dysplasia is the most likely cause and prompt treatment can improve long-term prognosis.
Shoulder OCD risk is 23x higher than average, but shoulder OCD is significantly less common than elbow dysplasia.
Panosteitis causes waves of pain and lameness, which can switch between limbs. Possible triggers include consumption of protein-rich, high-calorie commercial puppy food. Breed risk in Rottweilers is 1.4x average.
Fragmented sesamoid bones are frequently present without being the cause of lameness. Elbow dysplasia should be ruled out before making a definitive diagnosis.
-
Rottweilers are ranked #2 for elbow arthritis in a UK database. Elbow arthritis secondary to elbow dysplasia gradually worsens with age. The best treatment depends on age and arthritis severity.
Rottweilers are ranked #5 for malignant bone cancer. Affected dogs have an average age of 7.9y.
Athletes have a higher risk of muscle and ligament injuries. Elbow dysplasia should be ruled out before making a definitive diagnosis. Diagnosis can be challenging because x-ray changes are often present in Rottweilers without shoulder pain.
-
Panosteitis causes waves of bone pain and lameness which can switch legs. Breed risk is 1.4x higher than average.
Hock OCD causes chronic lameness, pain and swelling of one or both ankle (hock) joints. Breed risk is over 200x higher than average.
Hip dysplasia is common, but mild and moderate hip dysplasia rarely trigger insurance claims in Rottweilers with lifetime cover. Severe hip dysplasia triggers a claim in 12% of insured Rottweilers.
-
Cruciate ligament injuries are the commonest cause of chronic hindlimb lameness. Rottweilers were ranked #2 for cruciate ligament surgery (TPLO) in a UK hospital database. Tap here to learn more about how to diagnose and treat ACL injuries.
Cruciate ligament injuries are commonly present in Rottweilers with a prior diagnosis of hip dysplasia. Mild hip dysplasia is rarely significant.
Adult-onset patellar luxation is rare unless it has been triggered by cruciate ligament injury.
Rottweilers are ranked #5 for malignant bone cancer. Affected dogs have an average age of 7.9y.
Intermittent severe pain and lameness could be caused by lower back or Achilles problems.